Warning Signs of Astigmatism and How to Treat It
July 10, 2024
Have Any Questions?
Please contact us, if you have any queries
Categories

Astigmatism is a common vision condition that results from an irregular curvature of the cornea or lens, causing blurred or distorted vision. This can affect both near and far distances, making it crucial to understand the warning signs and available treatments to maintain clear vision and overall eye health. At Rani Menon Maxivision, we are dedicated to helping our patients manage their eye conditions effectively.
What is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea or lens in the eye has an uneven shape, which prevents light from focusing properly on the retina. This results in light rays being spread out, rather than converging to a single point, leading to blurry or distorted vision. Astigmatism can occur on its own or alongside other refractive errors like nearsightedness or farsightedness.
Warning Signs of Astigmatism
Recognizing the early signs of astigmatism can facilitate timely intervention and management. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred Vision: One of the most noticeable signs of astigmatism is blurry or distorted vision at all distances, which can make daily activities like reading or driving challenging.
- Eyestrain: Experiencing frequent discomfort or eyestrain, especially after prolonged use of digital devices or reading, can indicate astigmatism.
- Headaches: Regular headaches, particularly after visual tasks, may suggest astigmatism.
- Squinting: Squinting is often a response to blurred vision, as individuals attempt to see more clearly.
- Difficulty with Night Vision: People with astigmatism may find it difficult to see well at night, with glare and halos around lights becoming more pronounced.
- Double Vision: Blurred vision can sometimes cause double vision, especially in cases of significant astigmatism.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult an eye care professional to determine the cause and discuss appropriate treatment options.
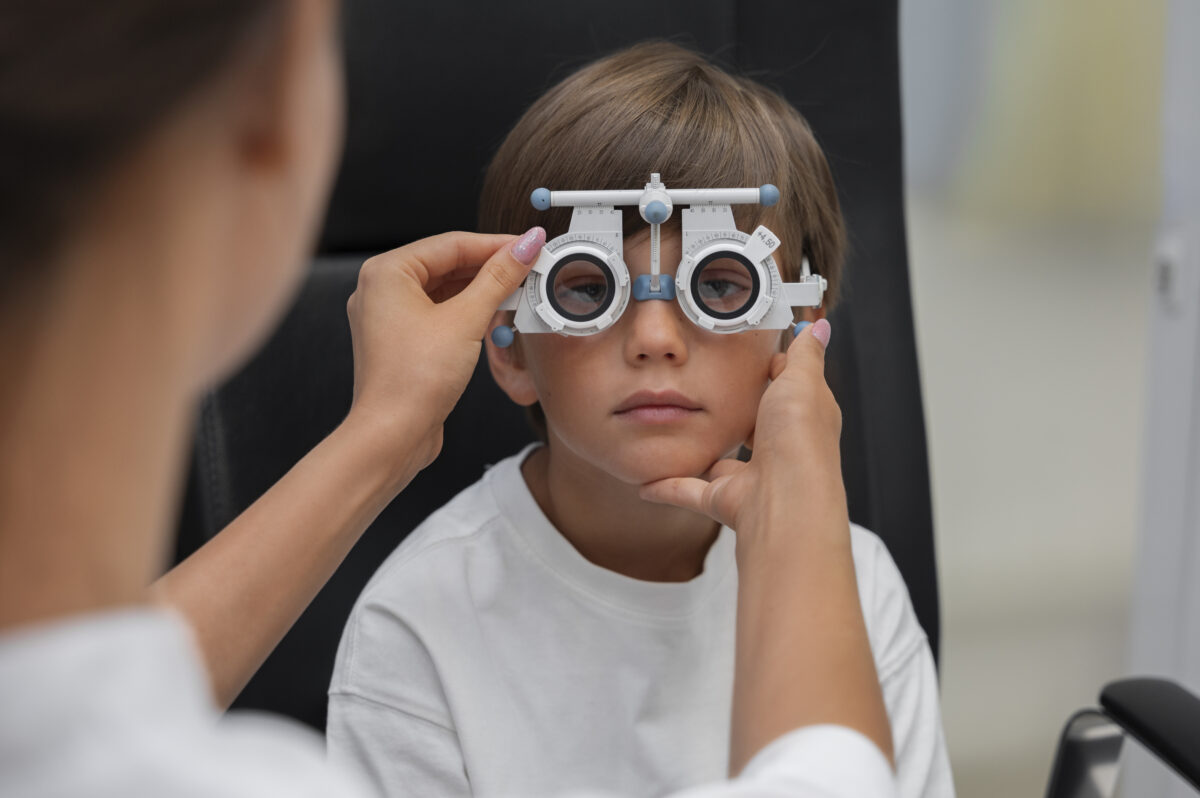
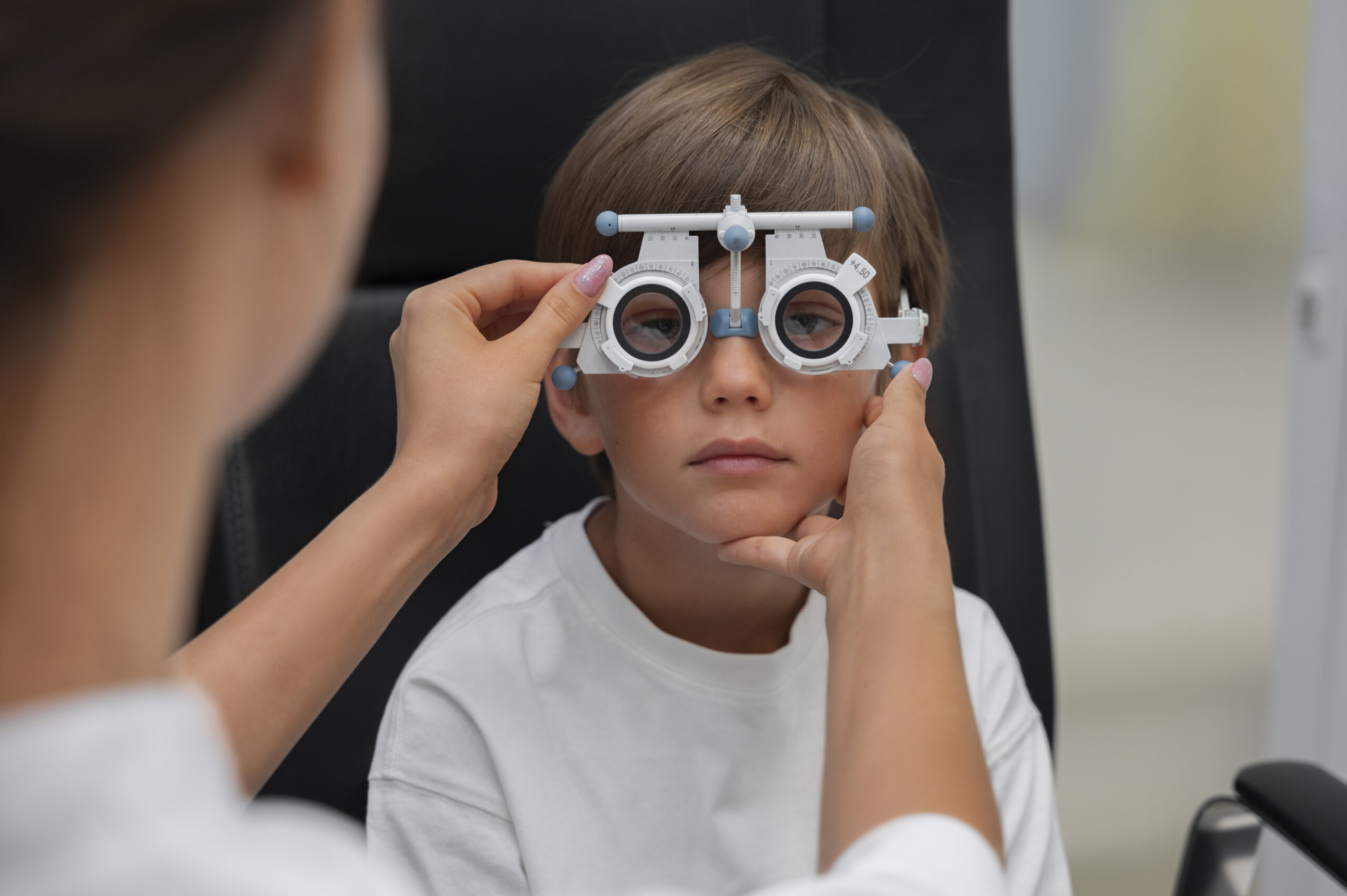
Diagnosing Astigmatism
Astigmatism is typically diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination. During this exam, an eye care professional will:
- Measure Your Visual Acuity: Assess how well you can see at different distances.
- Conduct a Refraction Test: Determine the prescription needed to correct your vision.
- Use a Keratometer: Measure the curvature of the cornea to detect astigmatism.
- Assess the Retina and Optic Nerve: Ensure there are no other underlying eye health issues.
These tests help in determining the degree of astigmatism and planning the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Astigmatism
Astigmatism can be corrected through various methods, depending on the severity and individual needs of the patient. The primary treatment options include:
- Eyeglasses: Specially designed lenses can correct astigmatism by compensating for the irregular curvature of the cornea or lens. These lenses focus light correctly on the retina.
- Contact Lenses: Toric contact lenses are specifically designed to correct astigmatism. These lenses have different powers in different meridians to address the irregular curvature of the cornea.
- Refractive Surgery: Procedures like LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) can reshape the cornea to correct astigmatism. Other surgical options include PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy) and LASEK (Laser Epithelial Keratomileusis).
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K): This method involves wearing specially designed rigid contact lenses overnight to temporarily reshape the cornea, providing clear vision throughout the day without the need for glasses or contacts.
- Lens Implants: In some cases, lens implant surgery may be an option, especially for individuals with high degrees of astigmatism or other refractive errors. This involves replacing the natural lens with an artificial one that corrects astigmatism.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the severity of astigmatism, age, lifestyle, and overall eye health. At Rani Menon Maxivision, we offer personalized care and treatment plans tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient. Our experienced doctor will discuss the best options based on the specific characteristics of your astigmatism and your visual requirements.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are crucial for the early detection and management of astigmatism. These exams help monitor changes in your vision and adjust your treatment as needed. It is recommended to have an eye exam every one to two years, or more frequently if you experience symptoms of astigmatism or other vision issues.
Conclusion
Astigmatism is a common condition that affects the quality of vision, but it can be effectively managed with the right treatments. Whether through corrective lenses, contact lenses, or surgery, there are several options available to help you achieve clear, comfortable vision. At Rani Menon Maxivision, we are committed to providing comprehensive eye care and assisting our patients in finding the best solutions for their vision needs. If you notice symptoms of astigmatism, please don’t hesitate to schedule an eye exam to discuss your options and take the first step toward clearer vision.