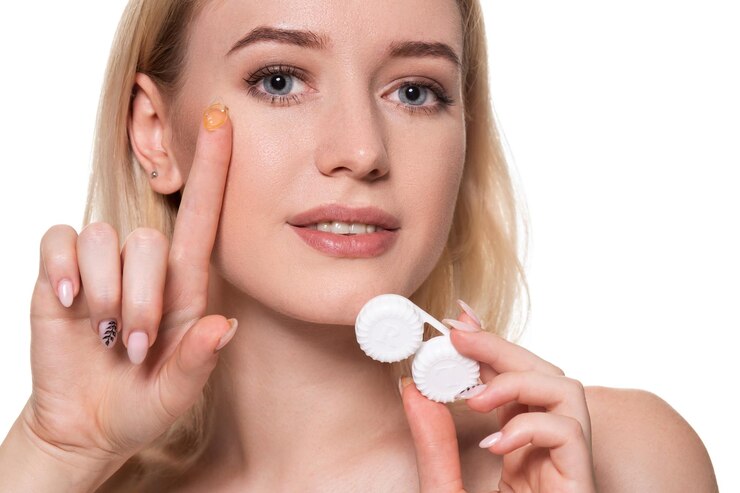
Contact lenses have revolutionized the way we correct vision, offering a sleek and convenient alternative to traditional eyeglasses. They provide an expansive field of vision, eliminate the nuisance of fogging, and cater to those with active lifestyles. However, despite their advantages, improper use of contact lenses can lead to severe complications that impact not only eye health but overall well-being. This article explores the risks associated with improper contact lens use and offers vital tips for ensuring safe and effective lens care.
Decoding Contact Lenses
Contact lenses are delicate, curved discs designed to rest on the cornea, the eye’s outer layer. Crafted from various materials, these lenses address common vision issues such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism, and presbyopia. They provide a broader visual field than glasses, reduce the inconvenience of fogging, and allow for greater freedom in physical activities. However, maintaining eye health requires careful usage of these lenses.
Common Mistakes in Contact Lens Usage
- Overextending Wear Time
Some contact lenses are approved for extended wear, meaning they can be used overnight or for several days. However, even these lenses have limits. Wearing them beyond the recommended duration can deprive the cornea of necessary oxygen, leading to discomfort, redness, and an increased risk of infections. Always follow the prescribed wear schedule to avoid these issues.
2. Improper Cleaning and Disinfection
Thorough cleaning and disinfection are crucial to prevent eye infections. Using tap water, saliva, or homemade solutions for cleaning lenses can introduce harmful microorganisms, leading to conditions such as bacterial keratitis. Always use the recommended cleaning solutions and adhere to the hygiene practices advised by your eye care professional.
3. Neglecting Regular Lens Replacement
Contact lenses have an expiration date. Using them past their intended lifespan can impair oxygen permeability, cause lens deposits, and increase the risk of infections and irritation. Regularly replacing lenses as instructed by your eye care specialist is essential for preserving eye health.
4. Exposure to Water
Water from swimming pools, hot tubs, or showers can contain harmful microorganisms that pose a threat to eye health. Contact lenses should never come into contact with water, as it can result in severe infections and corneal damage.
5. Lens Sharing
Sharing contact lenses is highly discouraged. Each person’s eyes have unique characteristics, and using someone else’s lenses can transfer harmful bacteria, viruses, or contaminants. Always use your own lenses and avoid sharing them.
6. Sleeping with Contact Lenses
Unless specifically designed for extended wear, sleeping with contact lenses is not recommended. Tear production decreases during sleep, which can reduce oxygen supply to the cornea and increase the risk of infections and corneal swelling.
Potential Risks and Complications
- Eye Infections
Improper contact lens use can lead to various eye infections, including bacterial, fungal, or viral conditions such as conjunctivitis, keratitis, and corneal ulcers. These infections can cause pain, redness, light sensitivity, and, in severe cases, vision loss. Regular eye exams and proper lens hygiene are key to preventing these issues.
2. Corneal Hypoxia
Extended wear or failing to remove lenses during sleep can lead to corneal hypoxia, a condition where the cornea does not receive enough oxygen. This can cause corneal swelling, blurred vision, and discomfort. Adhering to recommended wear times and lens care practices can help prevent this problem.
3. Corneal Abrasions
Improper handling or fitting of contact lenses can lead to corneal abrasions, or scratches on the cornea’s surface. This can result in pain, sensitivity, and an increased risk of infection. Ensuring a proper fit and handling of lenses is crucial to avoid abrasions.
4. Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis (GPC)
GPC is an allergic reaction to protein deposits on contact lenses or poor lens hygiene. It causes itching, redness, and mucus discharge. Maintaining proper lens cleanliness and hygiene can help prevent GPC.
5. Dry Eye Syndrome
Contact lenses can aggravate dry eye symptoms. Extended wear and improper care can deplete the tear film, leading to discomfort, irritation, and potential corneal damage. Using lenses with higher oxygen permeability and applying preservative-free lubricating eye drops can alleviate these symptoms.
6. Vision Distortion
Ignoring lens replacement schedules can lead to blurry vision, ghosting, or distorted images due to lens deterioration and deposits. Regularly replacing lenses ensures clear vision and eye comfort.
Essential Guidelines for Safe Contact Lens Use
- Consult an Eye Care Professional
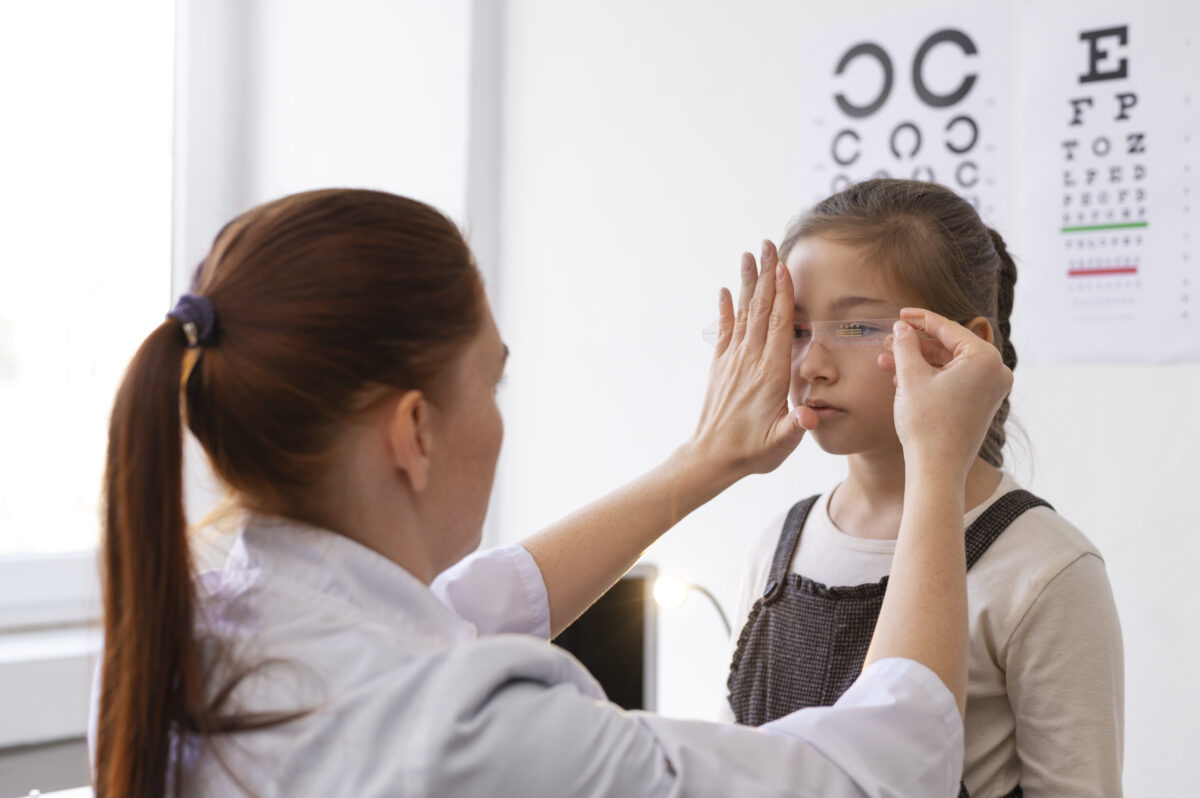
Before starting contact lenses, schedule a comprehensive eye exam and fitting with an eye care professional. They will determine the right type and prescription of lenses suited to your needs.
2. Maintain Proper Hygiene
Always wash your hands with soap and water before handling contact lenses. Avoid using lotions, creams, or perfumes on your hands, as these can transfer to the lenses and cause irritation.
3. Adhere to Replacement Schedules
Replace your contact lenses according to the schedule recommended by your eye care professional and the lens manufacturer. Never wear expired lenses.
4. Use Recommended Cleaning Solutions
Clean and disinfect your contact lenses with solutions recommended by your eye care professional. Avoid homemade or improvised solutions, as they may not be effective.
5. Remove Lenses Before Sleeping
Unless explicitly prescribed for extended wear, always remove your contact lenses before sleeping to ensure proper oxygen supply to the cornea.
6. Avoid Water Contact
Keep your contact lenses away from water. Never swim or shower with them on, as water can introduce harmful microorganisms.
7. Do Not Share Lenses
Avoid lending or borrowing contact lenses. Each person should have their own properly fitted pair to prevent contamination and infection.
8. Schedule Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are essential to monitor the health of your eyes and ensure that your contact lenses fit correctly.
Conclusion
While contact lenses offer unparalleled convenience and visual freedom, improper use can lead to serious eye health issues. By following the essential tips outlined in this blog and maintaining rigorous hygiene and lens care practices, you can enjoy the benefits of contact lenses while protecting your vision. Always prioritize your eye health and consult an eye care professional for any concerns or questions about your contact lenses. Your eyes are precious—take the necessary steps to keep them healthy and safe.
If you encounter any issues or discomfort with your contact lenses, or if you need expert advice on maintaining your eye health, Dr. Rani Menon Maxivision Eye Hospital is here to assist. Contact us today to schedule an appointment with our skilled team and ensure your eyes remain healthy and your vision stays clear.









 Introduction
Introduction