Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Care
April 25, 2024
Have Any Questions?
Please contact us, if you have any queries
Categories
Living with diabetes entails a vigilant awareness of its potential complications, and one such concern is diabetic retinopathy. This condition affects the eyes, posing a risk to vision and overall eye health. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and proactive measures to manage diabetic retinopathy.
Causes of Diabetic Retinopathy:
Diabetic retinopathy is a result of damage to the blood vessels in the retina caused by high levels of sugar in the blood over an extended period. The condition progresses in stages, from mild non-proliferative retinopathy to severe proliferative retinopathy. As the blood vessels weaken, they may leak fluid or blood, affecting vision.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Blurred Vision: As the condition advances, vision may become blurry due to swelling or the development of fluid in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision.
- Floaters: Patients may notice dark spots or ‘floaters’ in their field of vision, caused by the bleeding of damaged blood vessels.
- Impaired Color Vision: Colors may appear faded or different, signifying damage to the retina.
- Vision Fluctuations: Vision may vary, especially in different lighting conditions.
Managing Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial in preventing and managing diabetic retinopathy. Regular monitoring and adherence to a diabetes management plan are essential.
- Regular Eye Exams: Diabetic individuals should undergo comprehensive eye exams at least once a year. Early detection allows for timely intervention and better outcomes.
- Blood Pressure Control: Managing blood pressure is equally important, as high blood pressure can exacerbate retinopathy.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, contributes to overall well-being and can positively impact eye health.
In the event of diagnosed diabetic retinopathy, various treatment options exist, including laser therapy and medications. Timely intervention can prevent further progression and preserve vision.
Conclusion:
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious concern but can be managed effectively with proactive measures. Regular eye check-ups and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle play pivotal roles in preventing and mitigating the impact of this condition.
In Thrissur, Kerala, individuals seeking expert care for diabetic retinopathy can turn to Dr. Rani Menon Maxivision Eye Hospital. Dr. Rani Menon, a seasoned ophthalmologist, specializes in diabetic eye care and offers comprehensive solutions for various eye conditions. Contact Dr. Rani Menon Maxivision Eye Hospital in Thrissur for personalized care and expertise in managing diabetic retinopathy. Prioritize your vision and embark on a journey towards eye health and well-being.
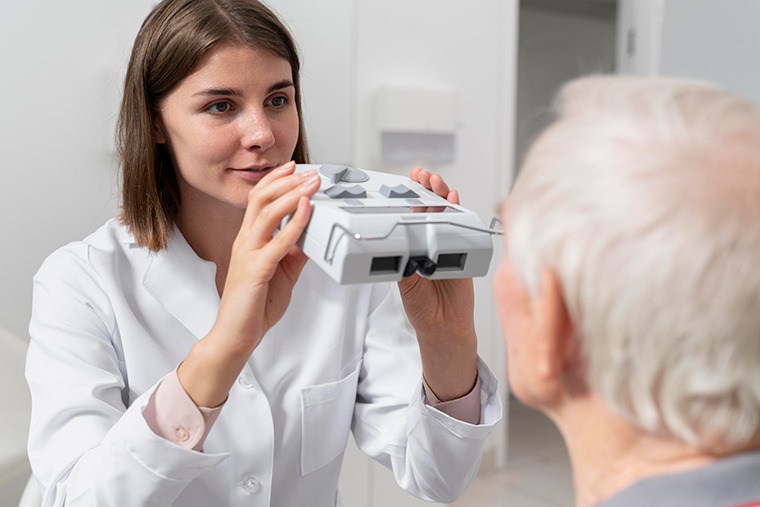



 Living with diabetes and vision requires constant vigilance over various aspects of your health. While most individuals are familiar with the impact of diabetes on blood sugar levels and organ function, it’s crucial not to overlook its effects on vision. Diabetes can significantly impact eye health, leading to complications that may result in permanent vision impairment. In this blog, we will explore three ways diabetes can affect your vision and the importance of regular eye check-ups.
Living with diabetes and vision requires constant vigilance over various aspects of your health. While most individuals are familiar with the impact of diabetes on blood sugar levels and organ function, it’s crucial not to overlook its effects on vision. Diabetes can significantly impact eye health, leading to complications that may result in permanent vision impairment. In this blog, we will explore three ways diabetes can affect your vision and the importance of regular eye check-ups.